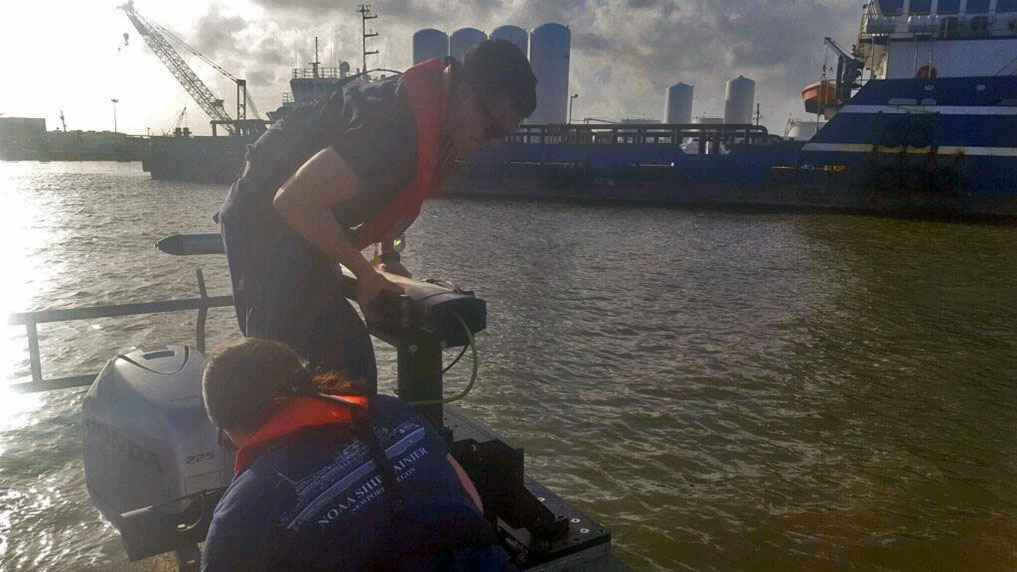
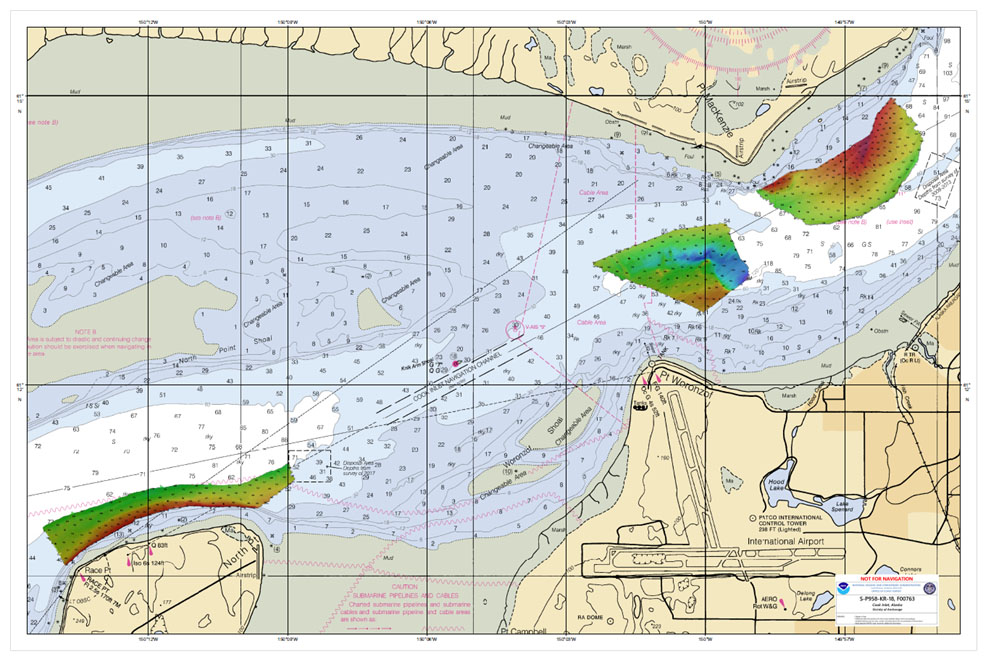
By Lt. Cmdr. Bart Buesseler
At 8:29, on the morning of Friday, November 30, 2018, a magnitude 7.1 earthquake shook Anchorage, Alaska, for thirty stressful seconds. It was the largest earthquake in Anchorage since the Good Friday Quake of 1964, and brought Alaska’s most populated city to a standstill as residents evacuated buildings and came to terms with what they had just experienced.
Continue reading “One year later – Coast Survey’s response to the Anchorage earthquake”